Like most investors, I am a little too obsessed with unicorns.
But not just the Silicon Valley kind. As the mother of a five-year-old daughter, my interests also veer in a pink, sparkly direction. So it should not be all that surprising that I recently found myself in a dusty corner of the internet where die-hard unicorn fans go to spread their wings.
It was there, deep in the My Little Pony forums, that one question stopped me in my tracks: “is a male alicorn possible in the future?1”
An alicorn, for those uninitiated to the mythological particulars, is the rare winged, female version of a traditional unicorn.
My Little Pony popularized the term, and the fan forum on which user “Green Precision” asked his question back in 2015 had some interesting answers to the particulars of this philosophical dilemma.
Shadow Stallion responded immediately, “I don’t think a male Alicorn will be possible in the future. Not because its [sic] not wanted or because its [sic] not genetically possible…but generally when male characters are introduced to a show where female characters are prominent, things get ugly.”
Malinter posited, “they probably do but given the female-to-male ratio of Equestria2 they are probably exceptionally rare. The real problem for a male alicorn is not that they exist but where is their place in the world? …Our male alicorn has some pretty big hoof prints to fill in while at the same time not make a trainwreck of established lore.”
Wind Chaser went straight from unconscious bias to conscious bias in their response: “aesthetically a male alicorn just wouldn’t look right, because their bodies are already naturally larger than females, thus the wings would cause an imbalance to the design.”
But it wasn’t all bad news.
“Until it’s proven otherwise, it’s safe to say that something like a male alicorn is possible,” responded Geek0zoid. Crysahis agreed. “Overall yes, I believe there could be a male alicorn it may just take a while to actually happen!”
It doesn’t take a PhD in philosophy from Stanford or the one lone female investing partner at Sequoia3 to posit that these same conversations were probably happening all over Sandhill Road in December of 2009, as male VCs discussed whether female unicorns could actually happen4.
As we move into 2020, though, we’re about to see a pink, winged stampede.
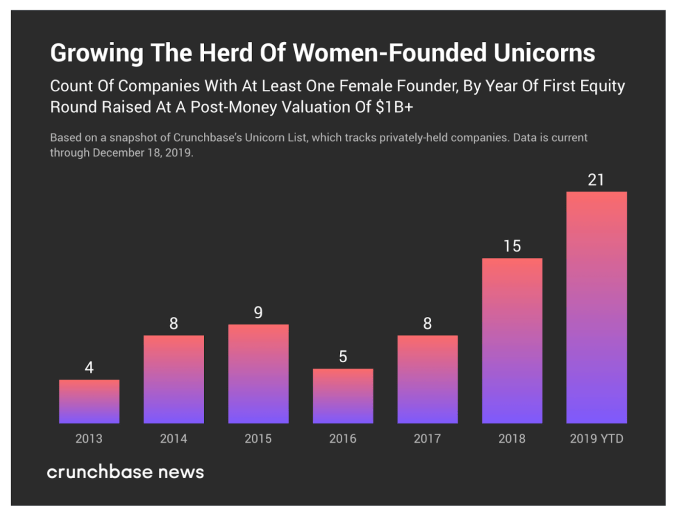
Just look at the recent trends. In 2019, more female-funded unicorns were born than ever before.5 And things are only looking up. (I’m looking at you, ClassPass!)
Public opinion agrees. Alongside TruePublic, where I am an advisor and angel investor, I ran a study asking if people believed we would see more female-led unicorns in the 2020s.6 At the time of this article, 68% of the 6,500 respondents said they believed we would see more, with 30% of women responding “many more” (as opposed to only 16% of men). Only 4% of women, but 9% of men, responded “no, not a chance.”7
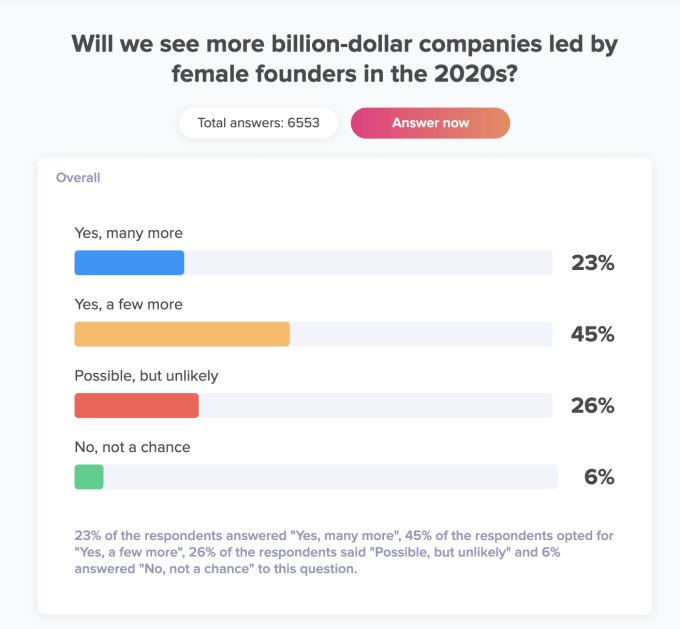
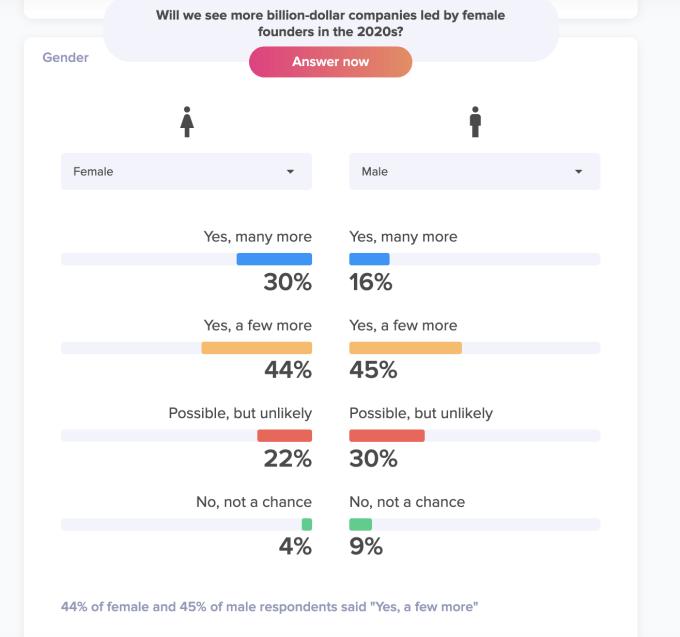
Kaben Clauson, founder and CEO, says “to represent Gen Z, Millennials and Gen X, TruePublic needs a weighted sample of roughly one thousand Americans to represent that population of the USA.” This particular study already has 6,500 respondents, making it statistically significant.
In fact, female-founded and female co-founded companies are actually over-indexing for unicorn status despite a lack of investment dollars.
Shelby Porges, co-founder of The Billion Dollar Fund for Women, explains: “Recent tracking has shown that female-founded companies represent 4% of all unicorns. That’s astonishing considering that in the past couple of years, they have gotten only slightly more than 2% of all venture funding.” Porges, whose group has mobilized more than 80 venture funds to pledge to invest over a billion dollars into women-founded companies, continues, “It demonstrates why we say, ‘when you invest in women, you’re in good company.’ ”
Here are the three reasons I believe a herd of winged female unicorns (OK, alicorns) is coming down the pipeline in the 2020s:
1. Women invest in women at 3x the rate of men
New data reveals that women invest in women at nearly three times the rate that men do and with the (slow) rise in the number of female investing partners at VCV firms, we are poised to see more and more gender-balanced founding teams getting funding.8 Like one male GP at one of the world’s top VC funds said to me when discussing one of the few female partners at his firm, “she always brings us parenting companies.” It might be cringe-worthy if TechCrunch hadn’t declared 2020 “a big year for online childcare” and that same female partner weren’t about to make a big chunk of cash thanks to all the upcoming parenting alicorns she was smartly funding.
Sophia Bendz, a partner at Atomico who also leads the Atomico Angel Program, said, “I’m confident we’ll see more female unicorns in the next decade because there’s a growing wave of ambitious female founders building incredible products and services. There are also more women in VC now and I’ve seen first-hand the impact having female investment partners can have on increasing the amount of investment into female-led companies. The data shows that women invest in women at three times the rate as male investment partners.”
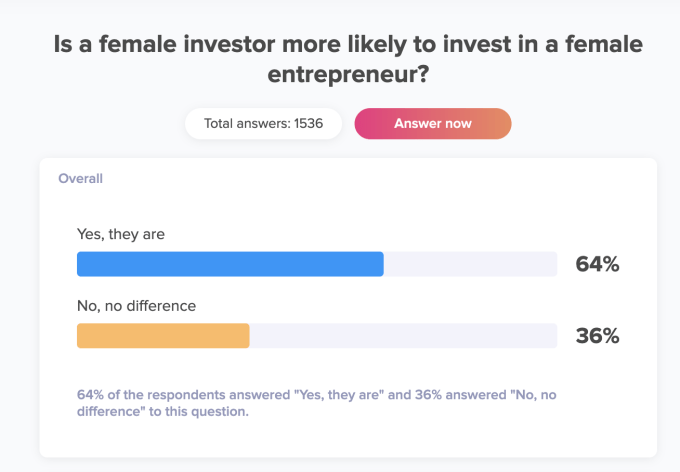
My study at TruePublic coincided with these findings. When asked if a female investor was more likely to invest in a female entrepreneur, 64% of people responded affirmatively (64% of these individuals were women and 63% were men).9
Jomayra Herrera agrees. An investor at Cowboy Ventures (which thanks to Aileen Lee coined the term “unicorn” in the first place), and a volunteer with AllRaise, a nonprofit promoting women in VC, she says: “As the venture industry continues to diversify, especially as it relates to gender and race/ethnicity, I am optimistic that we will see more female-led and people of color-led unicorns over the next decade. We know that diverse teams not only function better, but they are able to see areas of opportunities that more homogenous teams might miss. I think the next generation of investors are more likely to question conventional wisdom, forms of pattern recognition that may lead to bias, and other structural barriers that have historically left out promising entrepreneurs.”
Camila Farani is a well-known investor in Brazil. As founder of G2 Capital, former president of Gavea Angels and a personality on Brazil’s “Shark Tank,” she says “having diverse points of view at the table makes the decision clearer and more certain. People who think differently than you and have other visions of the market, sometimes can show you what you can’t see by yourself.”
She also reminds us not to forget the impact that angel investors can have. “The investments market is still made up mostly of men, but this landscape is changing gradually. It is interesting to see that angel investing is being the most common choice for women who want to make their first investments.”
This trend of investing more in women isn’t just limited to female investors. Susana Robles has spent two decades leading the charge to invest in women in Latin America and alongside Marta Cruz of NXTP Labs is co-founder of WeXchange, a platform that connects women entrepreneurs from Latin America and the Caribbean with mentors and investors.
As Robles says, “I think the world is finally waking up to the fact that there is serious research proving that startups with women co-founders win in all aspects: profitability, as well as greater social and environmental awareness. Investors should want to have this triple win.” She continues, “women tend to return money to investors faster than men, and at the same time, they obtain higher returns. Women are in charge of 64% of all global purchasing decisions on products and services, so having women on C-level positions increases the chance that a startup [will] be highly attractive to a massive market and become a unicorn.”
It also extends to the LPs in the funds. “I also think many investors in funds (mostly DFIs [development finance institutions] but not exclusively) have become more vocal in stating that they don’t want any more to invest in teams led by an all-white, all-male cast who choose startups with all-white, all-male founders.” Jennifer Neundorfer is the co-founder of Jane VC and an investor in Kinside, a parenting app that just raised a $3 million seed round. When describing her fund’s rationale for focusing on female founders, she drops the mic: “we’re going to invest in an under-looked asset class that is overperforming.” Boom.
2. Female founders are creating new billion-dollar markets
Another reason we’ll see more female-founded “alicorns” in the 2020s has everything to do with the new markets that female founders are creating. Hunter Walk of Homebrew was one of the initial seed investors in Winnie, an online marketplace for childcare that recently raised a $9 million Series A. At the time, he saw something that others investors didn’t. Winnie co-founder Sara Mauskopf explains, “Four years ago when we started Winnie, parenting and especially child care were not hot investment areas. This has been changing. It certainly helps that more investors are women and are in the thick of their child-bearing and rearing years.”
Part of what Walk says he recognized was the clear founder-market fit displayed by Mauskopf and her co-founder Annie Halsall. As Mauskopf says, “With Winnie, we saw an opportunity to solve the child-care crisis that other founders either did not recognize or did not care to solve. While everyone else was starting crypto and scooter companies, we were building the first-ever tech platform for $57 billion child care industry. Lack of access to quality child care disproportionately impacts women, so it shouldn’t be surprising that it took a female led team to capitalize on this opportunity.” Expanding on the concept of founder-market fit, Walk says, “I love to come away thinking, these are the absolute right founders to build this business.”10
Bendz, the Atomico partner who specializes in femtech and is also an avid angel investor, agrees. “Often I meet founders that you can tell are at the right place at the right time with the right mindset and the right team. It’s almost like all of the experiences they have had prior to launching a company have been preparing them to create that business at that time. These are the kind of founders who I know are in it for the long haul, and who are going to weather the ups and downs.” As a woman who uses the products and services she invests in, Bendz is also an example of investor-market fit, which I believe will open new markets in the decades to come.
Something else investors like Walk and Bendz believe in? Outsized opportunities. And the potential for outsized opportunities are especially ripe in untapped markets. The rise of femtech is yet another example of how the intuitive success of the concept of founder-market fit ultimately needed more female founders for certain markets to blossom. As Bendz explains, “Throughout a woman’s life there are many big events that have a big impact on our overall health — from childbirth to menopause. I know all women are tired of poor or non-existent solutions for women surrounding those life events, and that’s why we are seeing so many companies launching to better serve women’s needs. When you think about the fact that women have only had the right to vote and educate themselves for 100 years, it’s mind-blowing how long the world was operating with only 50% of the population in control. That’s reflected in the products and services we as a society have funded.”
Women’s consumer products are another area. Ornella Moraes is one of four female co-founders of Brazilian-led Sousmile, which recently raised a $6 million USD Series A led by Kaszek Ventures. “Our brand is a woman,” Moraes says of her dental beauty startup that retails throughout São Paulo. And so are the leaders of the company. At Sousmile, there are four female co-founders and two male co-founders. “More dentists in the world are women than men, so it’s been critical for our team to have more female founders,” she says. In this way, the rise of female founders and co-founders can completely change markets. “We believe this will fundamentally create a different type of product,” says Walk.
3. Emerging markets will take the lead
Finally, certain emerging markets pose a particular opportunity for female founders by over-indexing for both large IPOs and female founders. 2017 was the first year that more of the largest IPOs in the internet sector globally came from emerging markets. Nazar Yasin, founder of Rise Capital, which invests in emerging markets, says “This trend isn’t going away.” After all, most GDP growth comes from emerging markets, where most global internet users live. As he explains, “the future of market capitalization growth in the internet sector globally belongs to emerging markets.” And yet this type of innovation takes resilience. “If you’re a startup in one of these markets, it’s like trying to grow a plant in the desert.”11 In an environment that demands more daily resilience, there is a different appetite for risk and innovation. (I call this resilience innovation.)
Perhaps the easiest example of emerging market innovation fueled by resilience is fintech. Emerging markets and their often unstable economies boast a much higher number of frustratingly unbanked individuals. This brings about innovation. Hanna Schiuma, the Brazilian-born fintech founder of ElasBank, where I am an angel investor and advisor, explains how ubiquitous such fintech innovation is becoming.
“Soon all finance will be tailor-made and fintech will be common ground because all financial services will be technology-intensive.” She also argues that the nature of such an innovation allows the industry to become more innovative, and thus inclusive, which is exactly what is happening with her own women’s bank, launching in 2020. “That means great opportunities to better serve women’s financial needs to offer dedicated products, and to gather female talent to build those products from a diverse and innovative perspective.” Ultimately, “resilience is key for us to build that pool of talent and open the doors for gender balance and financial inclusion.”
Furthermore, data shows Africa and Latin America both beat global averages for percentages of startup female founders. Laura Stebbing is co-CEO of accelerateHER, a global community of leaders addressing the under-representation of women in tech through action. Raised in Southern Africa, Stebbing is passionate about Africa’s rise as a hub of female entrepreneurship.
“Africa has both the highest proportion of women founders at 26% [Latam comes in second]12 and a $42 billion funding gap. There’s clearly no lack of talent across Africa’s 54 countries, so for the investors, corporate executives, policy makers and established founders that aren’t moved by the moral arguments for gender parity, notice the enormous business opportunity. We will start to see a higher volume of resilient, scalable companies emerge as leaders build more diverse networks and ecosystems that support women to unlock their entrepreneurial potential.” Nathan Lustig, founder of Magma Partners, a VC firm in Latin America which invests in female founders above the regional average, explains, “investing in and empowering resilient women entrepreneurs is just good business, and is one of the biggest investment opportunities, especially in emerging markets.”
I believe Latin American can have an edge. I am a Silicon Valley-born investor now living in “Silicon Aires,” where I have been thrilled to see exciting numbers of female founders in Latin America. Susana Robles agrees, and says the reason is in part due to the nature of a committed ecosystem to support one another. “It’s the sheer need that forces you to collaborate.” An ecosystem like Silicon Valley doesn’t have the same need to do so. Of Latin America, Robles says, “In 10 years, we will have created a much more collaborative market than the developed ones.” And that collaboration is leading to great female founders. 2019, in fact, saw more funding going to female co-founders in Latin America than in Europe or the USA.13
This will lead to future alicorns. Ann Williams, COO of Creditas, a Brazilian fintech currently closing in on its own unicorn status, says “the conversion funnel for unicorns works just like any other selection process. We fill the top with a bunch of great women in supporting roles in emerging market startups, these women take their experiences and found rocking new companies. A percentage of these will convert to scaleups raising Series C and D rounds with valuations at $1 billion or higher. And voila! we get women-led unicorns.” She continues, “the odds are with us and I am sure the talent is too!”
Juliane Butty, startup head at Platzi and former regional manager of Seedstars, one of the leading accelerators and investors fostering female entrepreneurship in emerging markets, joins Williams. “We have definitely seen the rise of female founders and investors in emerging markets in the last decade. One supports the other. And we know that success breeds success.”
Perhaps My Little Pony fan Malinter said it best when he suggested how a male version of the alicorn could finally emerge in such a female-dominated space: “The simplest way they could probably add one in would be to make said alicorn the ruler of a neighboring nation.” In the same way, emerging markets may just hold the key for female unicorns.
No matter the region, Robles says “if we keep opening doors to women entrepreneurs who are as ambitious as men in growing their companies, we’ll begin to see many more unicorns with gender diversified teams.” Hanna Schiuma, the Elasbank founder who just might be building the next female-founded unicorn, agrees. “The alicorns are coming. And we’re ready to fly.”
2Equestria is of course where the My Little Ponies and their assorted unicorns, alicorns and friends all live.
3Go Jess Lee!
4Yes, Aileen Lee of Cowboy VC first invented the term in her 2013 TechCrunch piece, but we’re in a unicorn-fueled time machine, people.
8“Do Female Investors Support Female Entrepreneurs? An Empirical Analysis of Angel Investor Behavior,” Seth C. Oranburg, Duquesne University School of Law, Pittsburgh PA, USA and Mark Geiger, Duquesne University School of Business, Pittsburgh PA, USA
12Forthcoming research from TechCrunch/Crunchbase
13Forthcoming research from TechCrunch/Crunchbase










