In retrospect, 2019 feels like the working world’s last dance with spontaneity. The pre-pandemic past is rife with conferences, running into co-workers and post-work happy hours. Now, as companies such as Microsoft and Twitter declare remote work as the future, the very existence of physical offices is unclear for the long-term.
Yet, to a growing number of entrepreneurs in the Valley, when one physical door closes, a virtual one opens. With the goal of making remote work more spontaneous, there are dozens of new startups working to create virtual HQs for distributed teams. The three that have risen to the top include Branch, built by Gen Z gamers; Gather, created by engineers building a gamified Zoom; and Huddle, which is still in stealth.
The platforms are all racing to prove that the world is ready to be a part of virtual workspaces. By drawing on multiplayer gaming culture, the startups are using spatial technology, animations and productivity tools to create a metaverse dedicated to work.
The biggest challenge ahead? The startups need to convince venture capitalists and users alike that they’re more than Sims for Enterprise or an always-on Zoom call. The potential success could signal how the future of work will blend gaming and socialization for distributed teams.
Succulents and spatial technology
Companies within the virtual HQ world sit on a spectrum. On one end, there are the productivity companies, and on the other end, there are the video game companies. In the middle sits a mix between work and play, which is where Branch hopes to live.
There are more than 500 companies on Branch’s waitlist, and of current users, the retention has been 60% after a month of using the platform. So far, it has raised $1.5 million from investors including Homebrew, Naval Ravikant, Sahil Lavingia and Cindy Bi.
Walk through Branch’s virtual HQ and there are all the normal details you’d find in an office on Market Street: There are meeting rooms, lunch tables, a literal watercooler and, yes, succulents on your co-worker’s desk. Most employees log on for 12 hours, and for Election Day, they all had a watch party with a projected live stream in one area of the office.
The founder tells me that he’s hired people — and fired people — all in the virtual offices. Doors, he says, make a big difference.
The platform wasn’t built as a pandemic phenomenon, but in fact, was the result of years of experimentation by the founders, Dayton Mills and Kai Micah Mills. Both founders, since the age of 15, have spent time building Minecraft servers to sell to gamers, netting each thousands of dollars a month. In fact, Kai dropped out of high school to run Minecraft servers full-time, while Dayton tried at 13 to create his own game studio, even hiring an artist to do the illustrations. The game studio failed due to the fact that he was a “kid, 13, and had no money.”
“I spent the majority of my time online playing games with people. So my whole day was playing video games and having people to talk to in the background because I was on constant calls with people,” co-founder Dayton Mills said. “So for me, it’s not hard at all to use it. The question is can I get other people to think the same way?”
For now, Dayton Mills remains confident that his team’s platform will do well. After all, work is a non-negotiable place that you have to show up every day. And why not make that a little more fun?
“You can build a space where everyone comes to work,” he said. “Then after that, you can start building the spaces where they go after work. And it kind of spirals from there.”
Branch, like other virtual HQ platforms, is forced into an interesting spot of being both relevant enough to be used, but passive enough of an app to not feel like a burden. Dayton Mills says that this dynamic has made the team add features like no mandatory video or audio, and a talking icon per user to give the appearance of live interaction. The focus is to keep it casual so people can actually be online for six hours a day.
“People use Slack to work remotely but you go into a physical office and people are still using Slack, he said. The co-founder hopes the same for Branch, and has started measuring how many times people talk to each other in a given day. He says there are hundreds of chats per day, even if some are only for a few seconds.
The key technology that Branch and others are using to create spontaneity is spatial gaming infrastructure. At its core, the technology allows users to only hear people within their nearby proximity, and get quieter as they “walk” away. It gives the feeling of a hallway bump-in.
Dayton Mills thinks that the winning company in this crowded space is the one that can create a space that cultivates and sparks spontaneity.
“You can’t create the serendipity itself directly,” he said. “So create that environment.”
Gather, likely the largest virtual HQ platform out there, has embedded features to do what Mills is suggesting, such as “shoulder taps” to prompt a co-worker to chat, or pool tables where employees can circle around and start a virtual game of pool. The office tour included seeing a corgi on the desk, jack-o-lanterns and this reporter even added some floor plants to the set-up.
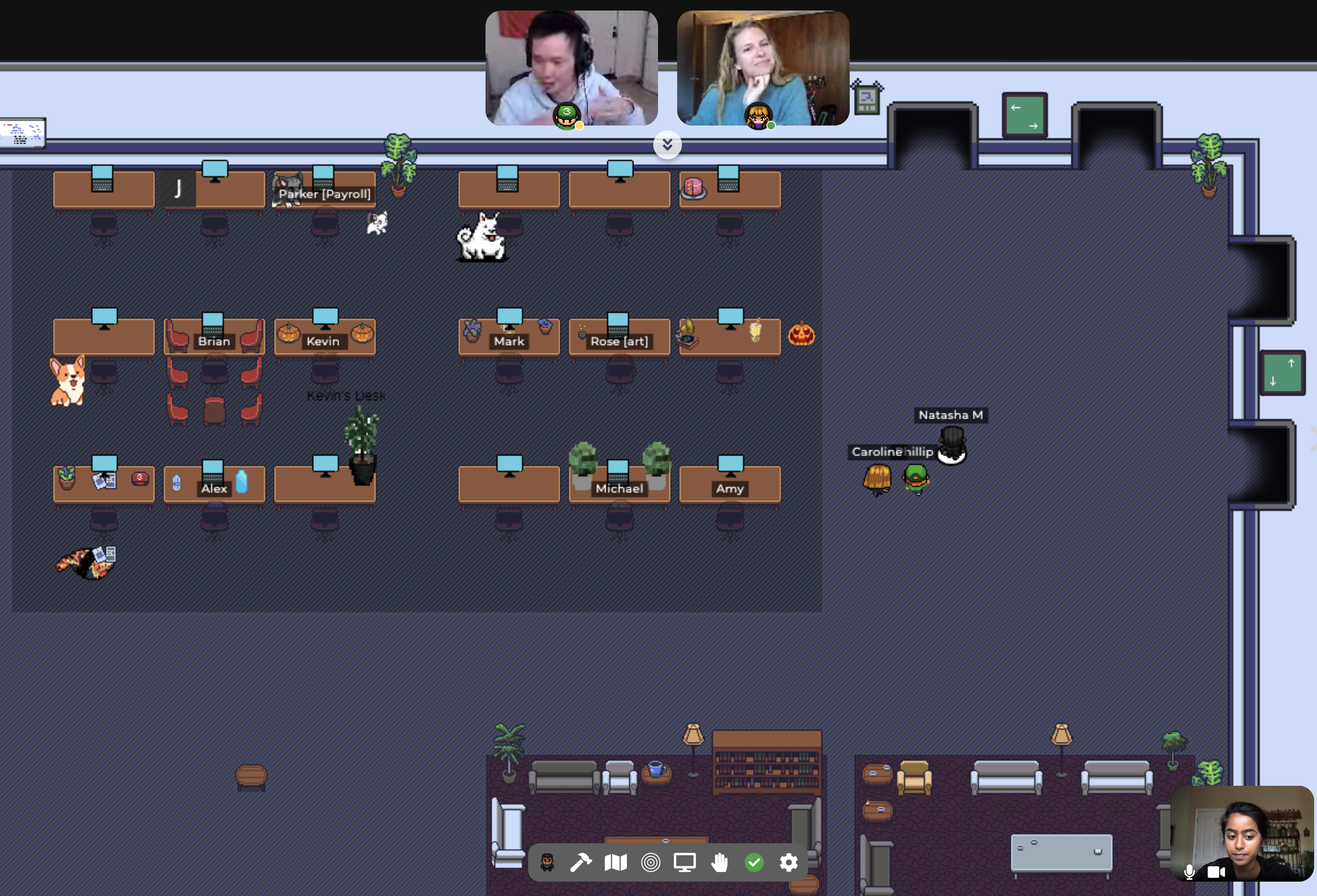
Gather’s main floor.
“You don’t need to worry about constantly worrying about if you’re being seen or not, but you will hear anyone who tries to come and talk to you,” said Phillip Wang, the founder of Gather.
The office design includes whiteboards and floating Google Docs to promote announcements and conversations.
Gather has been in the works for more than 18 months, since Wang and his friends graduated college. The team first tried to create custom wearables that would show you which of your friends were able to talk so you can tap into a conversation. When that didn’t work, they pivoted into apps, VR and full-body robotics. Then COVID-19 hit, and they saw an opening in the workplace.
Trillions, billions or none of the above?
Gather raised some money from angel investors, but has largely stayed away from institutional investors due to the potential of their cap table “biasing” the growth and direction of the company.
“You could easily end up in situations where the only options are ones you’re not happy with,” Wang said, of bringing VCs on at this stage. “We always want the way we make money to be aligned and incentivized to do good for our users.”
Angel investor Josh Elman tells me that many VCs are interested in the product, given traction and team, but also because virtual HQs have the potential to be more than just, well, virtual HQs. While offices are one space that the technology can occupy, the same base can be applied to schools, events, weddings and more.
To show potential, Elman nodded at Hopin, an online events platform that recently raised $125 million at a $2.1 billion valuation. It seems that most VCs agree there will be a number of winners in the events space, but it just comes down to the stickiness of the platform.
With the right value proposition, it’s not hard for people to understand multiplayer online gaming. For example, Epic Games’ Fortnite threw a psychedelic Travis Scott concert and more than 12.3 million people watched.
Thus, people are smart enough to understand gaming — but what about wanting to do it every single day with their colleagues, sans music and flashing lights? The total addressable market for professional, social gaming is murky. What if these platforms are a little bit more palatable as healthy businesses, instead of betting that the upstarts are a venture-backable business that could one day become a $100 billion business?
Image Credits: Bryce Durbin
Huddle’s Florent Crivello disagrees. He thinks the market opportunity for his company, an in-stealth remote HQ, is in the trillions because it has the potential to disrupt real estate, transportation and, in a macro sense, urban cities.
“I tell my former colleagues at Uber that I’m still working on transportation,” he said. “It’s just that the future of transportation is no transportation.”
Huddle has been in private beta for six months and is used by teams at Apple and Uber. There have been tens of thousands of hours of meeting on the platform, and Crivello says that some customers have stopped using Slack or Zoom altogether.
“The mistake they’re making at Slack is that there’s a difference between seeing a list of names on the screen and clicking on a name. And there’s a difference between seeing someone in the office and saying hi,” he said. “I think there’s something very human about the latter.”
Sahil Lavingia, the founder of Gumroad, got rid of Gumroad’s office in 2016, and says that they’re never going back.
“Offices are just too expensive and not necessary 40 hours a week,” he said. “I don’t think physical offices will go away, but they’ll be vastly diminished now that people know work can happen quite effectively, remotely. It’s also much cheaper.” Lavingia invested in Branch’s seed round.
Megan Zengerle, a partner at Sweat Equity who previously had a career in HR, said that companies considering virtual HQs should think about how long-term the solution is.
“Is that truly the culture you want to build for the company? Is that something that will serve the company long term? Is it logical sense to set up that way?” Zengerle said. “Culture is living and breathing, it’s not a static thing that you set and is done.”
Zengerle thinks that virtual HQs depend largely on the scope and product of the team. Most definitely, she does not think the solution is one size fits all.
“There’re a lot of playbooks coming out of the pandemic,” she said. “But the way you vary happens across each employee in the organization, much less organization by organization.”
These are the hurdles that have limited startups in the past, including 2011 TechCrunch Disrupt winner Shaker, from attracting a large customer base.
Before the pandemic, the world was not culturally ready for widespread remote work. Then, COVID-19 forced offices closed and employees adapted. These startups are betting that with the mass adaptation will come another cultural shift, one that could bring the metaverse into mainstream.