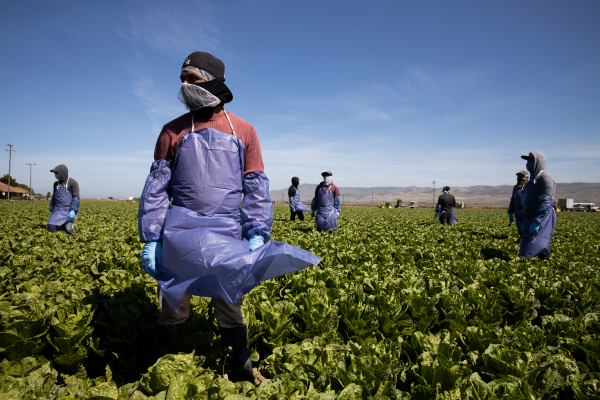
As the Biden administration works to bring legislation to Congress to address the endemic problem of immigration reform in America, on the other side of the nation a small California startup called SESO Labor has raised $4.5 million to ensure that farms can have access to legal migrant labor.
SESO’s founder Mike Guirguis raised the round over the summer from investors including Founders Fund and NFX. Pete Flint, a founder of Trulia, joined the company’s board. The company has 12 farms it’s working with and is negotiating contracts with another 46. The company’s other co-founder, Jordan Taylor, was the first product hire at Farmer’s Business Network and previously of Dropbox.
Working within the existing regulatory framework that has existed since 1986, SESO has created a service that streamlines and manages the process of getting H-2A visas, which allow migrant agricultural workers to reside temporarily in the U.S. with legal protections.
At this point, SESO is automating the visa process, getting the paperwork in place for workers and smoothing the application process. The company charges about $1,000 per worker, but eventually as it begins offering more services to workers themselves, Guirguis envisions several robust lines of revenue. Eventually, the company would like to offer integrated services for both farm owners and farm workers, Guirguis said.
SESO is currently expecting to bring in 1,000 workers over the course of 2021 and the company is, as of now, pre-revenue. The largest industry player handling worker visas today currently brings in 6,000 workers per year, so the competition, for SESO, is market share, Guirguis said.
America’s complicated history of immigration and agricultural labor
The H-2A program was set up to allow agricultural employers who anticipate shortages of domestic workers to bring to the U.S. non-immigrant foreign workers to work on farms temporarily or seasonally. The workers are covered by U.S. wage laws, workers’ compensation and other standards, including access to healthcare under the Affordable Care Act.
Employers who use the visa program to hire workers are required to pay inbound and outbound transportation, provide free or rental housing and provide meals for workers (they’re allowed to deduct the costs from salaries).
H-2 visas were first created in 1952 as part of the Immigration and Nationality Act, which reinforced the national origins quota system that restricted immigration primarily to Northern Europe, but opened America’s borders to Asian immigrants for the first time since immigration laws were first codified in 1924. While immigration regulations were further opened in the sixties, the last major immigration reform package in 1986 served to restrict immigration and made it illegal for businesses to hire undocumented workers. It also created the H-2A visas as a way for farms to hire migrant workers without incurring the penalties associated with using illegal labor.
For some migrant workers, the H-2A visa represents a golden ticket, according to Guirguis, an honors graduate of Stanford who wrote his graduate thesis on labor policy.
“We are providing a staffing solution for farms and agribusiness and we want to be Gusto for agriculture and upsell farms on a comprehensive human resources solution,” says Guirguis of the company’s ultimate mission, referencing payroll provider Gusto.
As Guirguis notes, most workers in agriculture are undocumented. “These are people who have been taken advantage of [and] the H-2A is a visa to bring workers in legally. We’re able to help employers maintain workforce [and] we’re building software to help farmers maintain the farms.”
Opening borders even as they remain closed
Farms need the help, if the latest numbers on labor shortages are believable, but it’s not necessarily a lack of H-2A visas that’s to blame, according to an article in Reuters.
In fact, the number of H-2A visas granted for agriculture equipment operators rose to 10,798 from October through March, according to the Reuters report. That’s up 49% from a year ago, according to data from the U.S. Department of Labor cited by Reuters.
Instead of an inability to acquire the H-2A visa, it was an inability to travel to the U.S. that’s been causing problems. Tighter border controls, the persistent global pandemic and travel restrictions that were imposed to combat it have all played a role in keeping migrant workers in their home countries.
Still, Guirguis believes that with the right tools, more farms would be willing to use the H-2A visa, cutting down on illegal immigration and boosting the available labor pool for the tough farm jobs that American workers don’t seem to want.

Photo by Brent Stirton/Getty Images.
David Misener, the owner of an Oklahoma-based harvesting company called Green Acres Enterprises, is one employer who has struggled to find suitable replacements for the migrant workers he typically hires.
“They could not fathom doing it and making it work,” Misener told Reuters, speaking about the American workers he’d tried to hire.
“With H-2A, migrant workers make 10 times more than they would get paid at home,” said Guirguis. “They’re taking home the equivalent of $40 an hour. The H-2A is coveted.”
Guirguis thinks that with the right incentives and an easier onramp for farmers to manage the application and approval process, the number of employers that use H-2A visas could grow to be 30% to 50% of the farm workforce in the country. That means growing the number of potential jobs from 300,000 to 1.5 million for migrants who would be under many of the same legal protections that citizens enjoy while they’re working on the visa.
Protecting agricultural workers through better paperwork
Interest in the farm labor nexus and issues surrounding it came to the first-time founder through Guirguis’ experience helping his cousin start her own farm. Spending several weekends a month helping her grow the farm with her husband, Guirguis heard his stories about coming to the U.S. as an undocumented worker.
Employers using the program avoid the liability associated with being caught employing illegal labor, something that crackdowns under the Trump administration made more common.
Still, it’s hard to deny the program’s roots in the darker past of America’s immigration policy. And some immigration advocates argue that the H-2A system suffers from the same kinds of structural problems that plague the corollary H-1B visas for tech workers.
“The H-2A visa is a short-term temporary visa program that employers use to import workers into the agricultural fields … It’s part of a very antiquated immigration system that needs to change. The 11.5 million people who are here need to be given citizenship,” said Saket Soni, the founder of an organization called Resilience Force, which advocates for immigrant labor. “And then workers who come from other countries, if we need them, they have to be able to stay … H-2A workers don’t have a pathway to citizenship. Workers come to us afraid of blowing the whistle on labor issues. As much as the H-2A is a welcome gift for a worker it can also be abused.”
Soni said the precarity of a worker’s situation — and their dependence on a single employer for their ability to remain in the country legally — means they are less likely to speak up about problems at work, since there’s nowhere for them to go if they are fired.
“We are big proponents that if you need people’s labor you have to welcome them as human beings,” Soni said. “Where there’s a labor shortage as people come, they should be allowed to stay … H-2A is an example of an outdated immigration tool.”
Guirguis clearly disagrees and said a platform like SESO’s will ultimately create more conveniences and better services for the workers who come in on these visas.
“We’re trying to put more money in the hands of these workers at the end of the day,” he said. “We’re going to be setting up remittance and banking services. Everything we do should be mutually beneficial for the employer and the worker who is trying to get into this program and know that they’re not getting taken advantage of.”